Pericoronitis: Symptoms, treatments, and complications
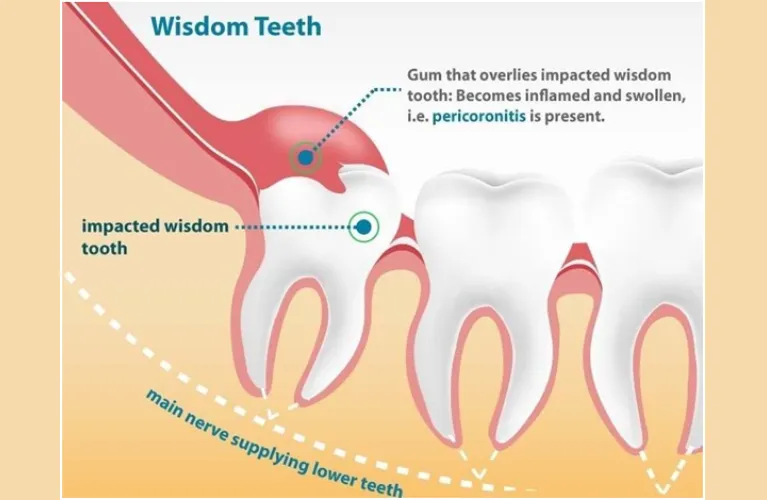
Pericoronitis is caused by the wisdom tooth’s lack of space. Because they may not penetrate the gums they can cause irritations and infections to soft tissues around the the wisdom tooth or teeth. If the wisdom teeth, tooth or teeth are not fully eruptible gums may appear in some cases. A flap is a place where the collects food particles can get stuck and bacteria accumulate, leading to infection.
The symptoms may vary between individuals if the infection is severe. The chronic symptoms typically last just one or two days and are persistent. Acute, more severe symptoms, will typically last three or four days, including:
What causes pericoronitis?
Partial tooth impaction is the main pericoronitis cause. When a tooth is partially trapped in soft tissue of your gums, bacteria can build up on opposing tooth and lead tooth infection due to swelling and inflammation of upper tooth.
How does pericoronitis affect my oral health?
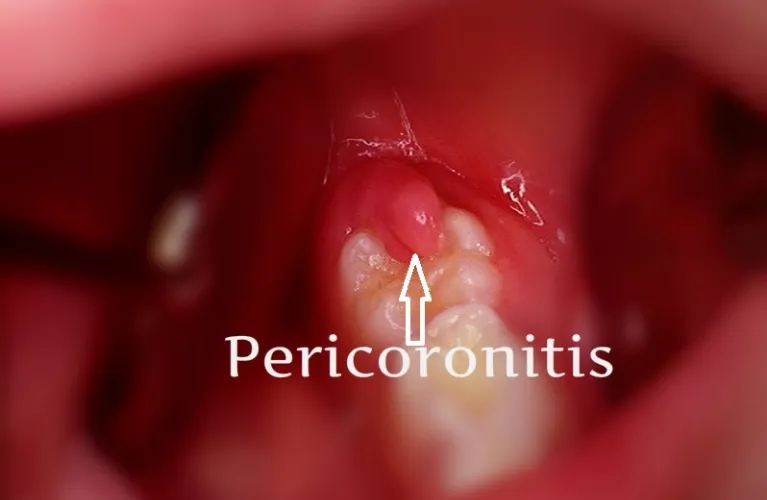
A gum flap may be created on an injured wisdom tooth too. These flaps swollen gum tissue — termed operculas – cover the soft tissue covering your upper wisdom tooth and gumline. In some cases food, toxins food debris can enter the operculus and cause infections.
What are the symptoms of pericoronitis?
Pericoronitis may be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term).
Acute pericoronitis symptoms may include:
- Fever.
- Severe pain around your back teeth.
- Redness and swelling of your gum tissue.
- Pus or drainage.
- Discomfort when swallowing.
- Lockjaw (trismus).
- Facial swelling on the affected side of the face
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck.
Chronic pericoronitis symptoms may include:
- Mild, temporary achiness near your back teeth.
- Bad breath (halitosis).
- A bad taste.
- dull pain
- swollen gum in the affected area
How common is it and who does it affect?
Pericoronitis can occur on wisdom teeth and affects people who have a few wisdom teeth, have wisdom tooth infection, or have wisdom teeth out. The condition usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 29. The sex is sex in equal terms.The sex is gender.
What factors could increase my risk of developing it?
You’re more likely to develop pericoronitis if you:
- Are in your 20s.
- Have wisdom teeth that haven’t fully erupted.
- Are under a lot of stress.
- Have excess gum tissue.
- Are pregnant.
- Have poor oral hygiene.
Is pericoronitis serious?
Left untreated, pericoronitis can develop into an abscess. When this happens, infection can spread to other parts of your body. In severe cases, it can even be life-threatening.
With treatment, people usually recover from pericoronitis in a week or two. It’s important to seek care early on, before things worsen.
How is pericoronitis diagnosed?
Pericoronitis is a condition characterized by inflammation spreading infection of the gum tissue soft tissues surrounding of a partially erupted tooth, most commonly the third molars (wisdom teeth and third molars). To diagnose inappropriate pericoronitis treatment and prevent pericoronitis further, a dentist or oral healthcare provider typically performs a clinical examination and may consider the following steps further treatment to prevent pericoronitis:
Medical History
The healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, including any pain or discomfort in the affected area, and ask about your dental and medical history.
Visual Examination:
The dentist will visually inspect your oral cavity, focusing on the affected tooth eruption the area. They will look for signs and symptoms of inflammation, redness, swelling, and the presence of an operculum (a flap of gum tissue partially covering the tooth).
Physical Examination:
The dentist may gently palpate the area around the affected tooth to assess tenderness, swelling, or the presence of pus.
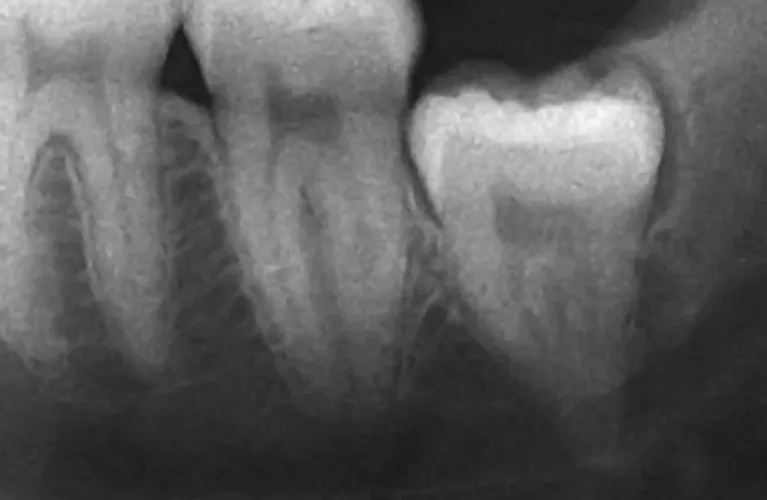
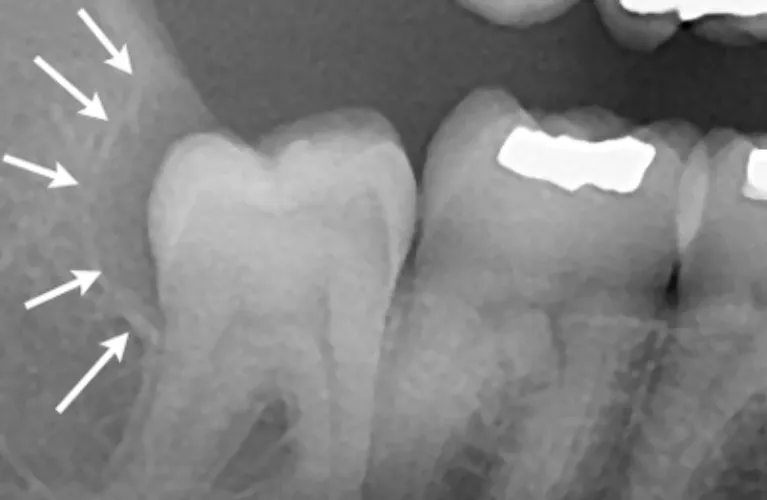
X-rays:
Dental X-rays or panoramic radiographs may be taken to evaluate the position of the tooth, its relationship to adjacent structures, and to determine if there are any underlying issues such as tooth impaction, tooth decay, or bone infections.
Symptoms Assessment:
The dentist will assess the symptoms involved tooth that you are experiencing, such as pain, swelling, or difficulty opening your mouth fully, to help confirm the diagnosis of tooth extraction.
How do you treat pericoronitis?
Medical Treatment
Dental Cleaning
During a dental cleaning, your dentist will use an irrigating solution to flush out any food particles, bacteria, or debris from the affected area. They may also prescribe medications, such as antibiotics or an antibacterial mouthwash, to address the issue.
Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics are sometimes prescribed to treat acute pericoronitis and infections. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and take the medication exactly as directed.
Prescription Mouthwash for Pericoronitis
To help eliminate harmful bacteria in your mouth, your dentist may recommend using a prescription mouthwash that contains chlorhexidine, a topical antiseptic. It is important to use the mouthwash as instructed, although temporary side effects of dental medicine like changes in taste or dental staining may occur, they are mild symptoms are typically short-lived.
Pericoronitis Removal Surgery
In many cases, if there is a gum flap (operculum) causing pericoronitis, your dentist may recommend its removal through a short oral surgery procedure. Sedation is available for minor oral surgery here, but often unnecessary. The procedure can usually be completed in less than an hour with the use of local anesthesia.
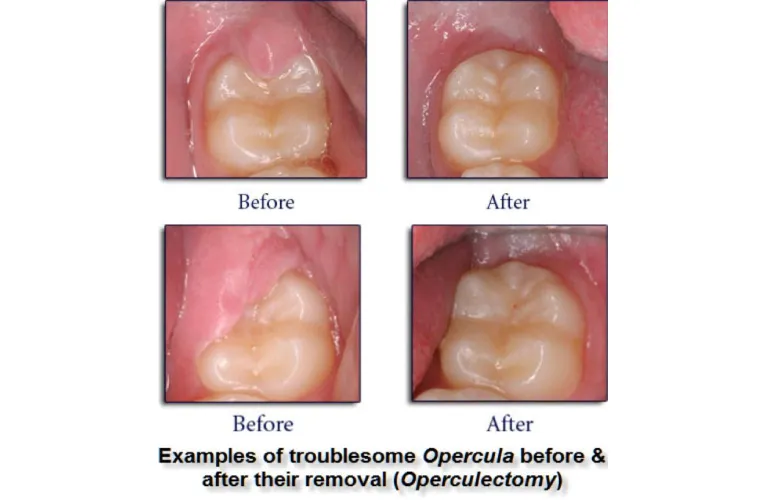
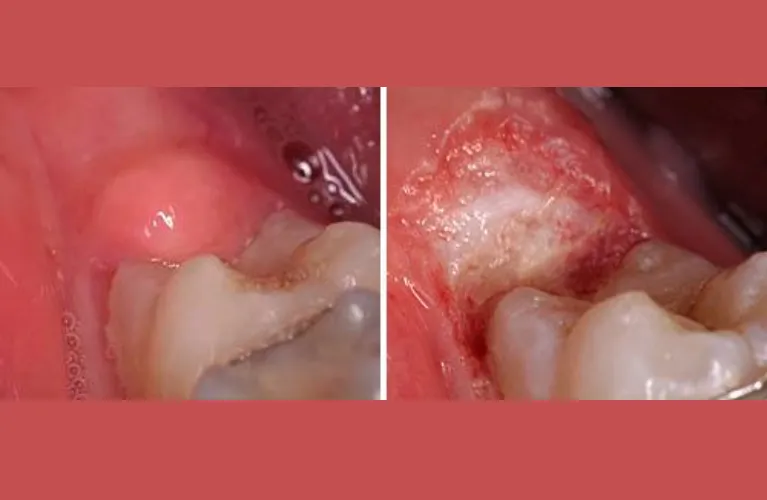
Wisdom Tooth Removal Surgery
If your wisdom tooth continues to cause chronic pericoronitis dental decay, and other problems, it may be necessary to have it removed. This procedure can be performed by an oral surgeon or periodontist with or without sedation.

Home Treatment
Although there are several home treatment modalities that the dentist may recommend, home treatment should not replace professional medical intervention. The dentist may prescribe home treatment modalities3 such as:
- Warm salt-water rinses (particularly after eating to remove food and debris)
- Oral water irrigation systems (using commercial equipment)
- Meticulous/regular oral hygiene (including brushing and flossing)
- Pain relievers (such as ibuprofen [Advil] or acetaminophen [Tylenol] or other over-the-counter pain relievers prescribed by the dentist).
Note: Avoid the use of hot compresses (which may increase the swelling) particularly for those with severe symptoms of pericoronitis such as fever or swelling of the neck or face)
Aftercare
If the wisdom tooth has been removed, it usually results in complete healing, and pericoronitis symptoms may subside within one to two weeks after surgery.3 Follow up treatment may include:
- Follow up appointments with the dentist or oral surgeon to monitor the rate of healing and level of tooth pain, if present
- Adhering strictly to aftercare instructions if a wisdom tooth was extracted (such as abstaining from smoking, eating soft foods, etc.)
- Home treatments (such as antibiotic oral rinsing, over-the-counter pain medication and more)
- Meticulous oral hygiene (including regular brushing and flossing)
- Quitting smoking (for those who smoke)
FAQ
Will pericoronitis go away on its own?
Unfortunately, pericaronitis is severe infection that cannot be eliminated by itself. In cases acute symptoms that are ignored this can become life threatening and dangerous. Generally, the tissue flaps must be removed as well as the lower wisdom teeth themselves. Infections can also require antibiotic treatment.
How serious is pericoronitis?
Pericoronite complications sometimes cause serious death. Untreated acute pericoronitis, is characterized by Ludwigs angina which spreads from mouth to tongue. This condition also leads to deep infection in the head and neck.
Can I ignore pericoronitis?
If a ruptured or untreated abscesses can spread to another part of your body, if acute infection is left untreated, it could be life threatening or deadly. A severe pericaronitis can cause complications including Ludwig’s Anagina – inflammatory rash which spreads into the rest of your head.
What is the best way to treat pericoronitis?
What should be done about eicoronitis? Your dentist oral surgeon will remove all food debris, and waste. The physician then recommends an antibiotic regimen in order to cure it with antibiotic. The nurse may suggest you use an antibiotic mouthwash to clean contaminated areas and eliminate the bacteria.
Can pericoronitis heal itself?
Unfortunately, the symptoms of pericoronitis often will never disappear. If pericoronitis treatment left untreated, this condition becomes dangerous within weeks or months. The soft tissue itself will typically require removal. If the same infection occurs and persists, antibiotics are also required.
Can I brush my teeth with pericoronitis?
If the condition occurs there are several ways you can treat it. Use brushes every other day if possible and floss regularly. Wash the face thoroughly using a chlorhexidine mouthwash.
Is pericoronitis very painful?
The most common complaint is an aggravated pain for several months, usually on the back. This has probably happened before and it is a little worse. It feels painful to swallow. It is a common feeling of unwellness.
Lor
