Sleep Apnea | TMJ Dentist In Vadodara – Aries Oro-Facial Dental
Unlocking the Secrets of Sound Sleep: Understanding and Managing Sleep Apnea
Sleep is a crucial aspect of our overall well-being, enabling us to recharge and rejuvenate. However, for millions of people worldwide, a sleep disorder known as sleep apnea compromises the quality of their sleep. It disrupts breathing during sleep, leading to a host of health complications. In this article, we will delve into the details of sleep apnea, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and effective management techniques to help you regain restful nights and improved overall health.

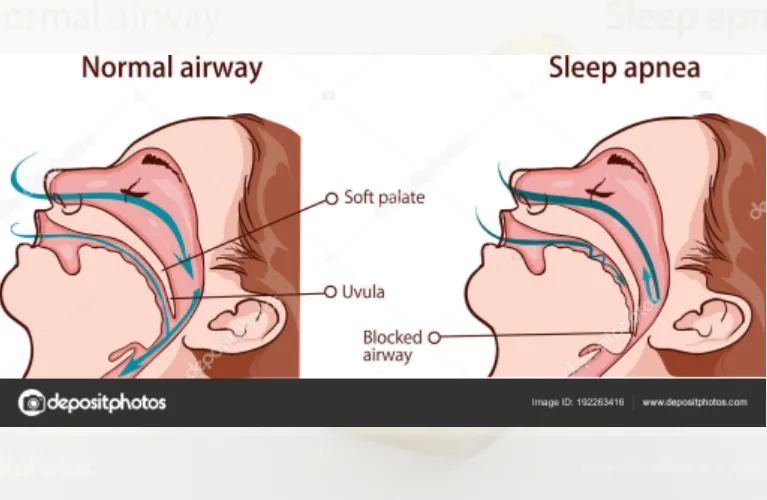
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a chronic disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses, called apneas, can last from a few seconds to minutes and occur due to partial or complete obstruction of the upper airway.
The most common type of sleep apnea is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where the airway collapses or becomes blocked, limiting airflow. Another less prevalent form is central sleep apnea (CSA), which occurs when the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe properly.
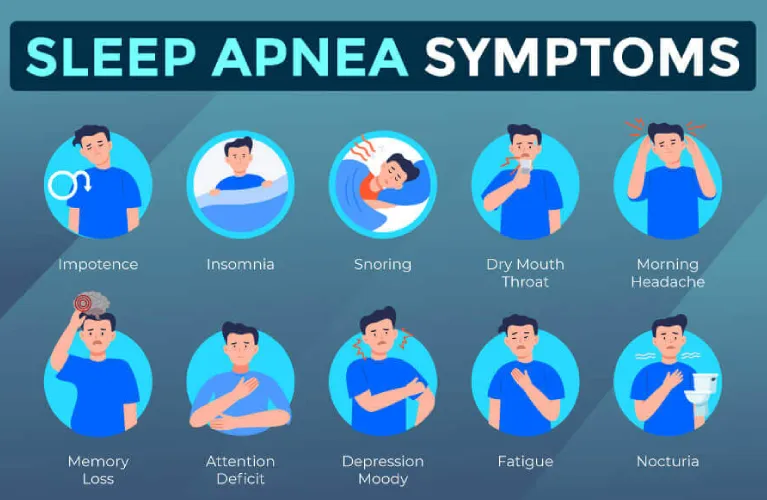
Recognizing the Symptoms
- Loud, chronic snoring
- Episodes of gasping or choking during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness or fatigue
- Morning headaches
- Poor concentration and memory problems
- Irritability and mood swings
- Night sweats
- Restless sleep or insomnia
- Frequent urination during the night
- Decreased libido
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of sleep apnea, including:
- Obesity: Excessive weight can lead to the accumulation of fat in the neck area, narrowing the airway.
- Age: Sleep apnea can affect individuals of all ages, but it becomes more prevalent as people grow older.
- Gender: Men are more likely to develop sleep apnea than women, although the risk increases for women after menopause.
- Family history: Genetic factors can predispose individuals to sleep apnea.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption: These habits can relax the throat muscles and contribute to airway blockage.
- Nasal congestion: Chronic nasal congestion, whether due to allergies or structural abnormalities, can hinder breathing during sleep.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional who specializes in sleep disorders. The diagnostic process typically involves:
- Sleep study: Polysomnography (PSG) is a comprehensive sleep test that monitors various physiological parameters during sleep. It helps identify the presence and severity of sleep apnea.
- Home sleep apnea testing: In some cases, a simplified sleep study can be conducted in the comfort of your own home, using portable monitoring devices.
Once diagnosed, an appropriate treatment plan can be formulated. Treatment options for sleep apnea include:
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP therapy is the gold standard treatment for sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a continuous stream of air pressure, keeping the airway open.
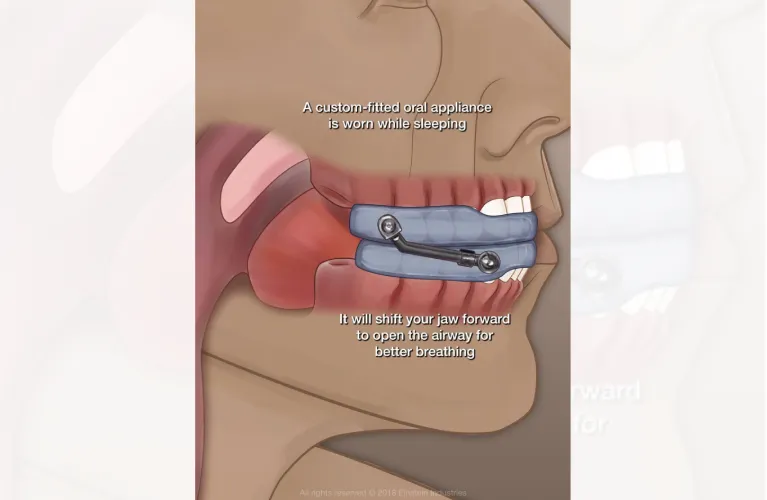
Oral appliances: Dentists can provide custom-fit oral appliances that reposition the jaw and tongue to maintain an open airway.
Lifestyle modifications: Losing weight, avoiding alcohol and sedatives, establishing regular sleep patterns, and sleeping on your side can all help alleviate symptoms.
Surgical interventions: In severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical procedures may be recommended to correct anatomical abnormalities.
Addressing sleep apnea is of paramount importance due to its significant impact on both physical and mental health. Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. These pauses, known as apneas, can last for several seconds to minutes and occur multiple times throughout the night. Here are several reasons why addressing sleep apnea is crucial:
- Quality of Sleep: Sleep apnea disrupts the normal sleep pattern, preventing individuals from obtaining restful and restorative sleep. The repeated interruptions in breathing lead to frequent awakenings, resulting in fragmented and poor-quality sleep. As a result, individuals with sleep apnea often experience excessive daytime sleepiness, fatigue, and lack of concentration, affecting their overall well-being and quality of life.
- Cardiovascular Health: Sleep apnea has been strongly linked to various cardiovascular conditions, including high blood pressure (hypertension), heart disease, stroke, and irregular heart rhythms. The repeated drops in oxygen levels and the strain placed on the cardiovascular system during apneas can lead to increased blood pressure, inflammation, and oxidative stress, increasing the risk of developing cardiovascular problems.
- Risk of Accidents: Sleep apnea significantly impairs daytime alertness and cognitive function, making individuals more susceptible to accidents. Excessive daytime sleepiness can lead to drowsy driving, workplace accidents, and decreased performance in daily activities. Addressing sleep apnea can help improve alertness and reduce the risk of accidents associated with excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Mental Health: There is a strong association between sleep apnea and mental health disorders. Chronic sleep disruptions can contribute to the development or worsening of conditions such as depression, anxiety, and mood disorders. Additionally, untreated sleep apnea has been linked to cognitive decline, memory problems, and an increased risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
- Overall Health and Mortality:Sleep apnea has been associated with a range of health problems beyond cardiovascular and mental health issues. It is linked to metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. It can also contribute to obesity, as disrupted sleep affects hormones that regulate appetite and satiety. Furthermore, untreated sleep apnea has been associated with increased mortality rates, highlighting the importance of early diagnosis and intervention.
Addressing sleep apnea typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and regular exercise, and the use of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices or other treatments prescribed by healthcare professionals. By addressing sleep apnea, individuals can improve their sleep quality, protect their cardiovascular health, enhance mental well-being, reduce the risk of accidents, and promote overall health and longevity.
