Crossbite: What Is It and How Is It Treated? Braces | Invisalign Treatment In Vadodara | Orthodontist
Lingual crossbite, also called crossbite, has become commonly used when the mouth is misaligned, or malocclusion. Crossbite occurs when your front teeth overlap with your front teeth. This misalignment may affect oral hygiene and cause discomfort when chewing food. The following article covers some common causes and treatments for crossbite symptoms and their causes.
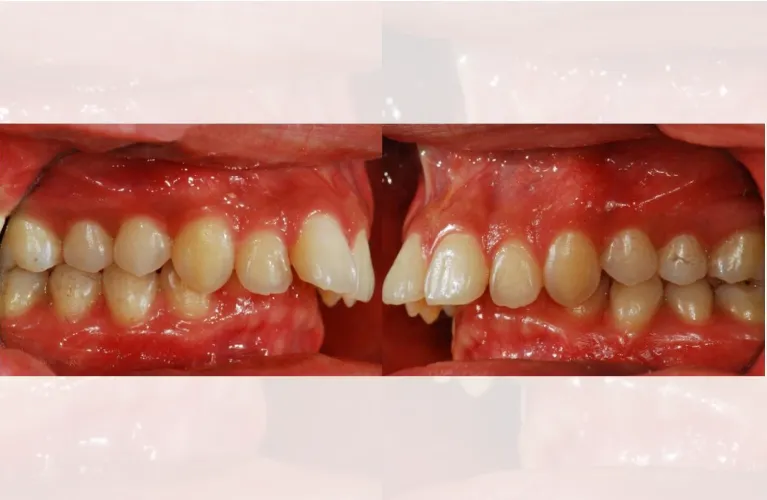
Anterior Crossbites
Anterior posterior crossbite occurs when the upper front teeth are positioned higher on top. The front teeth have 4 canines in the top teeth of each row. Anterior crossbites effect 4–5 people.
It is possible to treat them using orthodontic treatment, but in more severe posterior crossbite cases in adults, the posterior anterior crossbite may require surgery as a combined orthodontic treatment to remove the lower jaw to achieve optimal results.
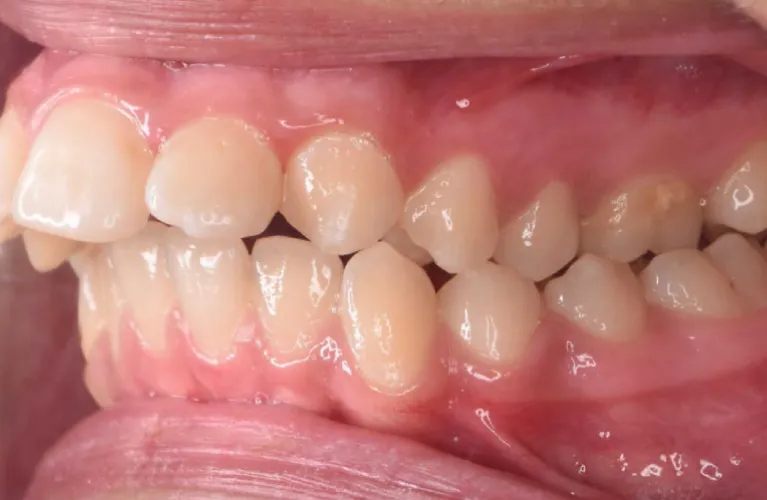
Posterior Crossbites
Posterior crosses are a bad bite at the rear teeth: the upper back teeth (the upper and lower teeth) reach farther out than the lower back teeth.
It can occur in unilateral posterior crossbite or in posterior crossbite and unilateral anterior crossbite bite, in either lateral or vertical directions.
Crossbites in posterior teeth effect 13% of the teeth and are corrected using orthodontic appliances known as expansion devices.
Overbite vs. Crossbite/Underbite
A well-balanced smile can cause a small over-bite with a healthy bite: the upper teeth overlap the bottom teeth and top teeth sit back. In an intermit, the opposite happens: the lower and top teeth will go over the upper ones, and it will be sluggish.
It may apply to an individual tooth or a section of a tooth. its overbites were too deep that needed correction. Crossbites and misaligned teeth also need to be fixed.
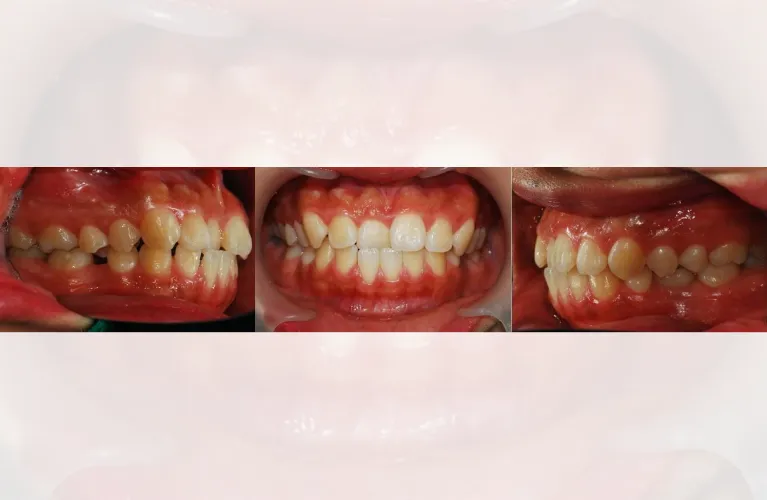
What Causes a Crossbite?
have two major reasons, Genetics & Development.
Similar to other physical features, the dental position and jawbone are inherited. Crossbite is genetic, and if your parents or grandparents have suffered from crossbite, then you are more likely to inherit the condition.
Jaw shape
- Genetic birth defects, such as cleft lip or cleft palate
- Overcrowded, abnormally shaped teeth
- Extra teeth
It’s not possible for children to inherit the traits of a parent, but some orthodontic care and treatment may improve them. Several things during dental development can cause a crossbite.
Various factors during dental development can cause a crossbite, including:
Missing teeth or jaw fractures resulting from accidents or injuries
- Ill-fitting dental crowns, dental appliances, retainers, or braces
- Tumors of the mouth or jaw
- Ectopically erupting teeth (teeth erupting in the wrong position)
- Thumb-sucking
- Mouth breathing
- Tongue-thrusting
- Prolonged use of a pacifier or bottle
- Losing the baby’s teeth too early or Delayed loss
- Growing the adult teeth
Signs and Symptoms of Crossbite in Adults
The presence of crossbite is also accompanied by dental mis asymmetry.
Headaches, toothaches, or jaw aches
- Pain when chewing or biting
- Trouble closing your mouth properly
- Speech impediments such as lisp or slurs
- Poor sleep quality
- Temporomandibular disorder (TMD)
- Pain in jaw joints or muscles
- Difficulty maintaining proper oral hygiene
- Bacterial growth
- Plaque build-up
- Cavities
- Gum or periodontal disease
- Tooth loss
Is a Crossbite Bad for Your Teeth?
What is a Crossbite? How To Diagnose, Treatment Methods, and More
How do we get a straight tooth? Perhaps your cross-bite is serious. A cross-biting disorder called an under bite can lead to rows of teeth being overextended in an improper manner.
Instead of a proper bite when the upper teeth and lower teeth are snugly connected with a small overbite the unilateral crossbite or under bite occurs when the lower teeth slide behind the upper teeth fit inside the top one or more teeth, either on the front or behind the back of other teeth.
Cross and under bites exist in several different ways. This guide will show you the symptoms of crossbones.
How to Treat Crossbites
it occur when the upper and lower teeth do not align properly when you close your jaw. There are different crossbites, including anterior crossbites (front teeth), posterior crossbites (back teeth), and unilateral crossbites (affecting one side of the mouth).
Treating crossbites typically involves a combination of orthodontic intervention and, sometimes, dental or surgical procedures.
Braces –
If you have a crossbite and need braces to correct it, it’s best to consult with an orthodontist.
They are dental specialists who can evaluate your specific case and provide you with the most appropriate treatment plan.
Crossbite occurs when your upper and lower teeth do not align properly, causing some of your teeth to be misaligned and affecting your bite.
During your initial consultation, the orthodontist will examine your teeth and jaw and may take X-rays or other diagnostic images to assess the extent of the crossbite. Based on the evaluation, they will determine the best course of treatment, which may involve braces.
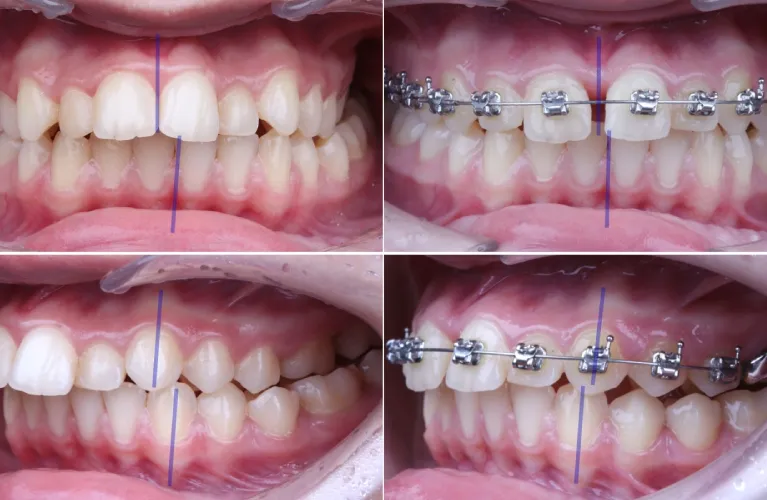
Demon Braces for Crossbite Management
Expanders
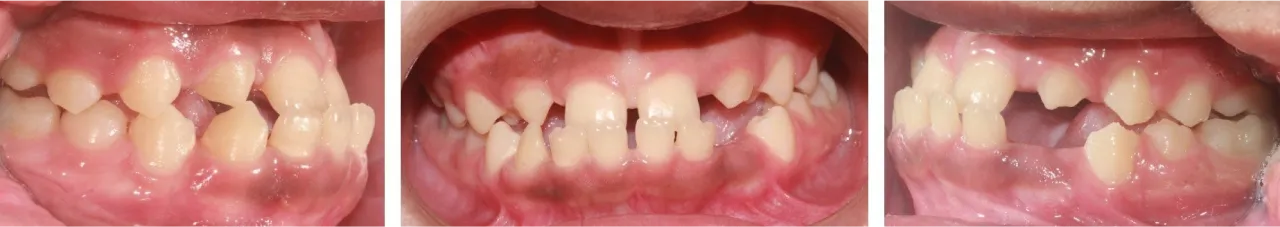
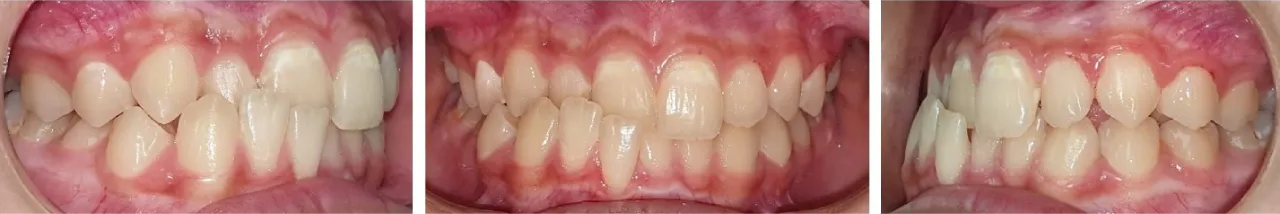
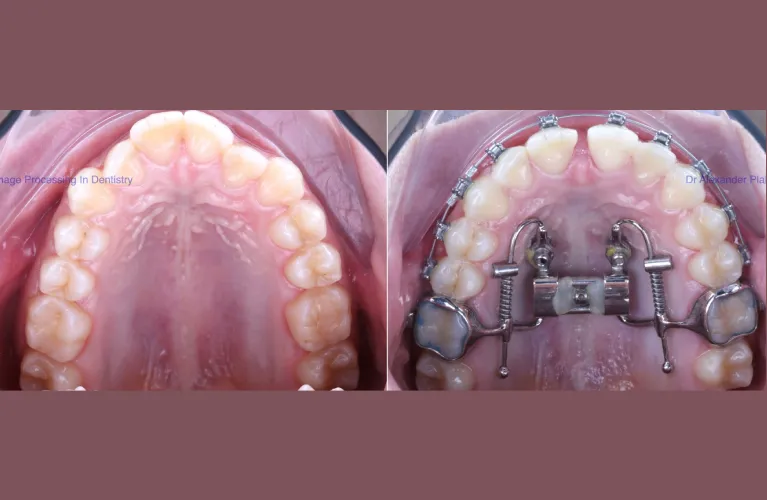
When patients present with constricted arches or posterior crossbites, upper expanders can improve upper arch form by expanding the teeth and dental arches.
Here, the patient initially had severe dental crowding. A palatal expander was used to correct the narrow arch, resulting in more room for blocked-out teeth.
Braces were then used to take advantage of the spaces created from expansion and all blocked out teeth were aligned with no need for extractions. Count the teeth, they’re all there!
Surgical periodontitis treatments
There are different types of surgical periodontal treatments, including:
Invisalign Clear Aligners
Invisalign treatments are highly effective methods to correct crossbites if a dentist has experience and training. Invisalign can only be used by experienced professional doctors.
Invisalign aligners are widely popular due to their ease of use and discreet and simple appearance. I believe Invisalign treatments have helped many people correct cross biting.
The Invisalign aligner is customized to the specific cases and the orthodontist will use 3D CAD technology to correct your bite.
Tooth Extraction
In severe cases, tooth extraction may be necessary to create enough space for the teeth to align properly. They usually do this before orthodontic treatment and in consultation with your orthodontist and dentist.
Jaw surgery:
For more complex or severe crossbites, orthognathic surgery may be required. This surgical procedure involves repositioning the upper or lower jaw to the correct position of the misalignment misaligned teeth.
Orthognathic surgery is typically performed by an oral and maxillofacial surgeon in collaboration with an orthodontist.
FAQ
What causes crossbite?
Tell me the cause of the crossbiting? A crossbite is often caused by genetic factors such as delayed loss of baby teeth or abnormal eruptions. Long actions such as sucking thumb or swallowing abnormally can create damage to the permanent teeth too. Teeth might go wrong; the bones could get distorted.
How do you correct a crossbite?
If serious crossbiting occurs the orthodontist may perform jaw re-alignment procedures. This adjustment adjusts the angle on the upper jaw. Aligner is a custom mouthpiece for each patient. It may also help cure crossbiting.
Can braces fix a crossbite?
Jaw surgery or tooth extraction are sometimes necessary posterior crossbite, but they are rare. Those suffering from crossbite can sometimes correct them through braces or by using palatal expanders.
What is crossbite problem?
Crossbite is an oral disorder that usually occurs when children begin getting teeth, or sometimes the alignment tooth position of baby teeth does not correct themselves when adults are born. If your tooth grows straight up and down the tooth can rotate to face the cheek or tongue as well.
How do you fix a crossbite on your teeth?
Braces are a widely used method of treating crossbite, but they can’t be your last choice. Your orthodontist might recommend a fixed or removable expanding device, or braces or plates for full anterior and posterior crossbite only, unilateral anterior and posterior crossbite only, or unilateral posterior crossbite for front-tooth injuries. Clear alignment is sometimes used in certain situations.
What is the cause of a crossbite?
It may be caused by tooth or skeleton problems or combinations thereof. The problem might result from habits and / or teeth loss, bone problems, airway issues, or genetic factors. Causes of crossbite include pacing, thumb and finger sucking, and tooth snapping.
Can crossbite be cured?
Crossbitte corrections usually require orthodontics and surgical procedures. In adult patients, crossbite treatment, is generally shorter if crossbones are severe than in children. It takes up to three years to repair crossbite.
What is the best treatment for a crossbite?
Braces treatment is effective and the best treatment for preventing crossbiting. One child under 7 can have crossbite treated with a brace. Braces are used as a tool for correcting correct a crossbite or jaw position.
What is the fastest way to correct crossbite?
Braces are commonly used for crossbitting and may not always the only choice you have to choose. You may have a fixed and removable expansion device in case of a posterior anterior crossbite as well as limited brackets or plates for a posterior anterior crossbite if required. Often it is possible to use alignment tape.
What age is crossbite treated?
The treatment for the cross-bite is important for prevention of the subsequent complications. Because kids’ jaws develop as a child they should correct a cross-bite by the ages of 7 to 12. During the younger age of 12 the chances for obtaining good results are very limited.
When is the best time to treat crossbite?
In the first two years of life, the jaw and cheeks will grow. In some cases a teenager is liable for a crossbiting. Unless the child has a more severe crossbite or over-bite the orthodontist may wait until the age of seven or eight years for treatment.
What is the reason for crossbite?
Cross-biting is usually associated with dental or skeletal problems with dental causes or combinations of these. This problem can result from habits, tooth growth delay, fractures in skeletal structures missing teeth, upper airways, or genetics. The cause for some crossbiting is the sucking on fingers or thumbs which push teeth forward.
What causes a crossbite?
How can crossbones occur? Crossbite can arise due to a genetic condition, delayed child teeth, or an errant permanent tooth. In addition single tooth only, prolonged movements of single tooth, such as sucking the tongue blade or swallowing the thumb could cause damage to the primary tooth. Teeth may be removed; bones may be dislocated.
Can a crossbite cause jaw problems?
A non-treatment crossbite could cause jaw pain or jaw pains such as Temporomandibular Joint Disorder (TMJ). A high force on the jaws may cause headaches or neck/shoulder irritation.
Is crossbite normal?
It is a cross-biting term for teeth whose upper and bottom teeth fit inside but don’t fit together when the mouth is closed. A full crossbite correction over-bite can affect your upper and bottom teeth, and cause the whole upper part to fall behind your upper and bottom teeth together. These conditions are widely recognized by dental orthodontists.
