Gum Swelling & Bleeding Gums Symptoms | Types | Symptoms | Causes | Diagnosis | Treatment
Often when we talk to our dentists we are looking to prevent cavities and gum disease. Obviously maintaining good oral health and maintaining good oral hygiene, you have to be mindful of the gums. Dental floss also provides important support for your oral and gum health, and overall wellbeing.
Generally, a gum bleed is indicative of gum disease. Some things can cause gums to become damaged. What is the cause of gum irritation? It is easy to treat and reduces the pain and swelling.
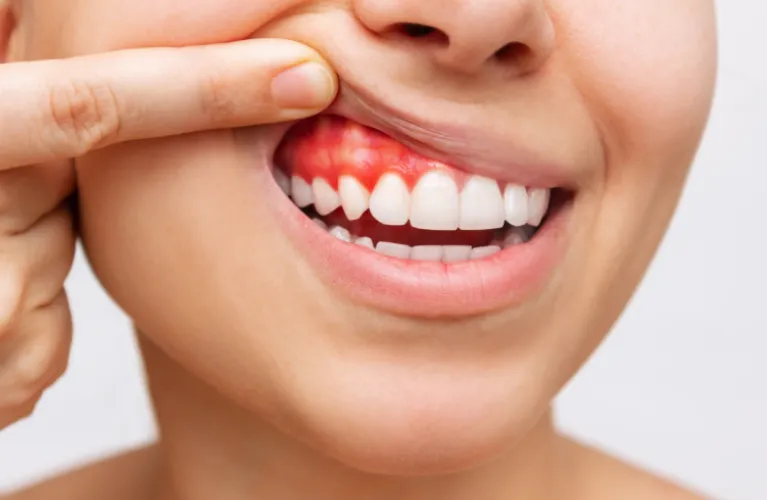

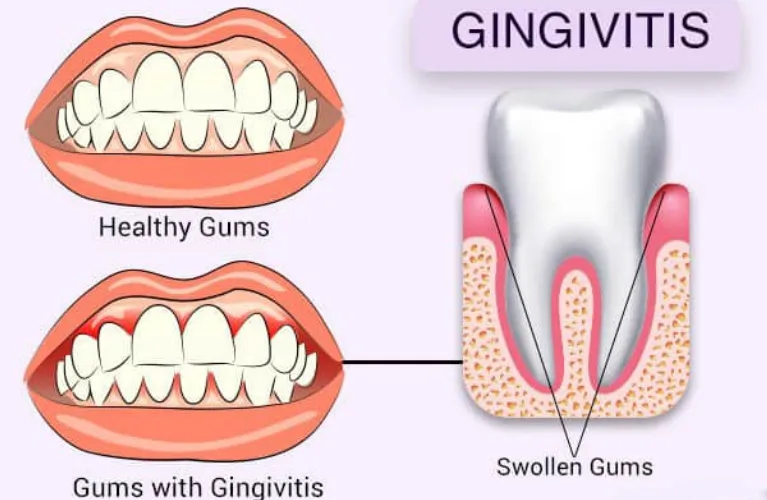
Causes of Gum Swelling and Bleeding gums
Swollen gums, also known as gingival swelling, can be caused by various factors. Here are some common causes cause of swollen gums:
Gingivitis:
The most common cause of red and swollen gums, is gingivitis, which is an early stage of gum disease. Poor oral hygiene, dental plaque, buildup, and bacteria can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation and swelling.
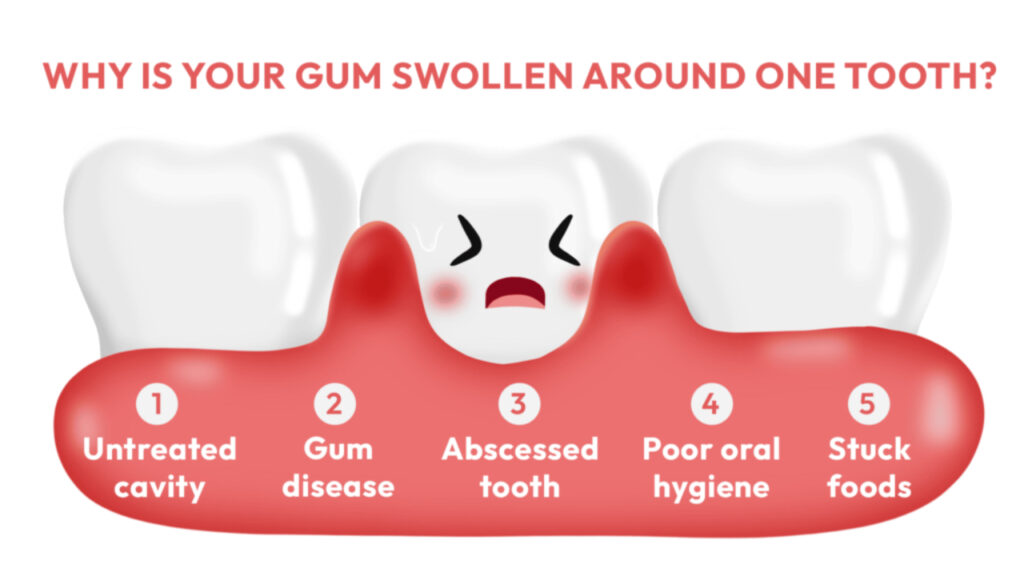
Periodontitis
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. Periodontitis causes the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating spaces cause swollen gums called periodontal pockets. These pockets can become infected, resulting in further gum inflammation bacterial infection and swelling.
Poor in oral health hygiene
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and regular dental cleanings can lead to plaque and tartar buildup on infected teeth. This buildup can irritate the gums, causing them to become swollen and tender.
Hormonal changes
Hormonal fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can make the gums more sensitive and prone to swelling.
Allergic reactions
Some people may have an allergic reaction to certain oral care products, such as toothpaste, mouthwash, or dental materials. This can cause gum irritation and swelling.

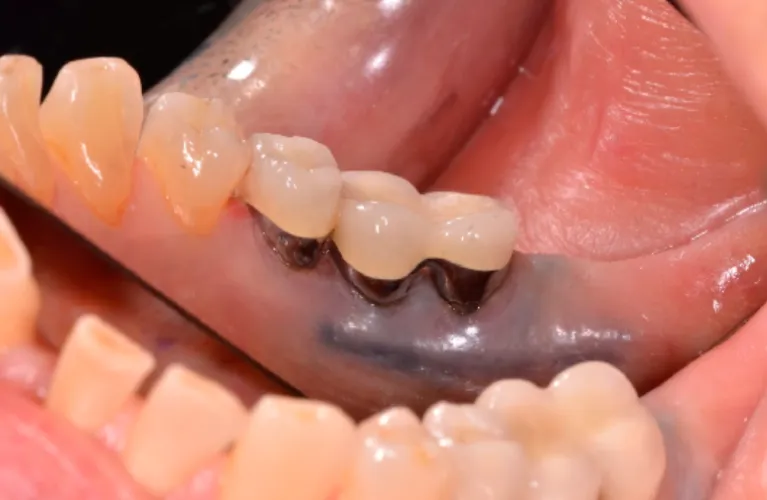
Dental infections
Infections in gum tissue around the gums or teeth, such as abscesses, can lead to gum swelling and pain.
Malnutrition
A lack of essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C and vitamin B, can contribute to gum problems, including swelling.
Certain medications
Some medications, such as anticonvulsants, calcium channel blockers, and immunosuppressants, may cause gum enlargement and swelling as a side effect.
Injury or trauma
Accidental injury or trauma to the teeth and gums themselves, such as from a toothbrush or dental instrument, can cause localized swelling.
Systemic conditions
Certain systemic health conditions that, like diabetes, leukemia, and autoimmune disorders, can affect the health of the teeth and gums, and lead to swelling.
It’s important to note that swollen gums can be a sign of an underlying dental or gum problem. If you are experiencing persistent or severe gum swelling, it’s recommended to see a dentist for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Gum Swelling and Bleeding gums
Swollen appearance
The gums may appear larger or puffy than usual. You might notice a change in their texture and shape.
Redness
Swollen gums often become red or darker in color compared to healthy gums
Pain or tenderness
It can be sensitive and tender to the touch. You may experience discomfort or pain while eating, drinking, or brushing your teeth.
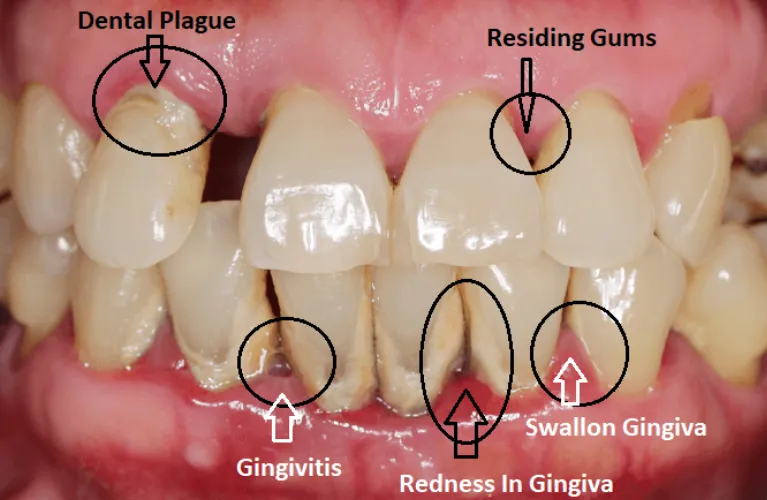
Bleeding
It may bleed easily, especially when you brush or brush and floss your teeth. You may notice blood on or rinse your mouth, toothbrush or in the sink after brushing.
Bad breath
It can contribute to persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth.
Receding of swollen gums
As the gums swell, they may start to pull away from the teeth, leading to gum recession. This can expose the tooth roots and cause increased sensitivity.
Formation of dental abscesses
In some cases, gum swelling can be accompanied by the formation of an a dental abscess itself, which is a pocket of pus. Abscesses are usually painful and require immediate dental attention.

Treatments Gum Swelling and Bleeding Gums
Medicated mouthwash may help treat swollen gums.
Medical treatment for swollen gums begins with seeing a dentist.
The type of medication or treatment the dentist recommends will depend on medical history and the underlying cause of tooth loss.
Medical treatments for oral issues may include various medical treatments:
- medicated mouthwashes
- ointments
- toothpastes

Prevention of Gum Swelling and Bleeding Gums
Taking steps to treat the cause of swollen gums and sore gums is a key part of any dental treatment.
These measures may help relieve pain, prevent swelling or ease the symptom:
What’s the best technique for brush and flossing my teeth?
Cleaning between your teeth is just as important as brushing. Floss can clean places that your toothbrush can’t reach. To floss properly:
- Break off about 18 inches of floss and wrap it around your middle fingers.
- Use your thumbs and forefingers to hold the floss tightly so there’s an inch or two of it between your fingers.
- Guide that middle section between your teeth, wrap the floss around one tooth (in a “C” shape), and rub up and down the length of that tooth seven to 10 times. (Note:Friction is necessary to remove plaque from your teeth surfaces. Water flossers are great for removing large pieces of food and debris. But if you use a water flosser, be sure you also use regular floss.)
- Now, wrap the floss around the neighboring tooth and repeat these steps.
If you haven’t been flossing, there might be some bleeding and discomfort for the first few days, but that should go away.
Use Inter Dental Brush
Use Inter Dental Brush
https://youtu.be/X7qrSmf4TYIhttps://youtu.be/EUMcom-Ew5Uhttps://youtu.be/GKxGV6gLEJw
Use a tongue scrapper
https://youtu.be/udX2GAJO_Ek
Use a Mouth wash
Avoid sugary drinks, as some research suggests they can contribute to bacteria buildup in the mouth.
Avoid tobacco, including smoking or chewing it.
Avoid alcohol and alcoholic mouthwashes, as the alcohol may dry out and irritate the gums.
Avoid sharp foods such as chips, seeds, and popcorn, which may get stuck in the teeth and cause severe pain afterwards.
It is important to note that these tips natural remedies are only supplements to a proper diagnosis and treatment of other symptoms of gum pain. Swollen or irritated gums typically signal an underlying issue or gum problems. Ignoring these symptoms may make the issue worse in the long term.
FAQ
How do you treat swollen gums?
How can a tooth be swollen by brushing or flossing? Rinse mouth several times a day in hot salt water. Applying a cold compress to the skin reduces inflammation.
It usually takes a few days to remove gum swelling. The swelling can cause gums to become inflamed.
What does gum swelling indicate?
it is often an indicator of gingivitis. Gingivitis causes swelling in the gums most commonly. The initial stage of gum disease is caused by bacteria buildout on gum surfaces and plaques.
How long do swollen gums last?
Swollen teeth cause swollen gums are common gum problems, and in some cases they don’t cause much concern. Occasionally swollen gums may show signs of gingivitis or periodontitis.
Having a painful mouth doesn’t help any way. The swelling or irritability of the gum is often accompanied by increased blood flow. When you look at your own swollen and sore gums or swollen gums, you can’t be certain they will get worse.
How can I reduce swelling in my gums at home?
How do I treat swollen teeth with salt? Use salt water to clean up any irritations in the eyes and mouth after drinking. Don’t bite them, don’t take them away. Do this twice daily until swelling disappears.
How can I treat inflamed gums?
Is there a treatment that can relieve a painful or sore gum? Using a gentle brush. Use water as a mouthwash to remove bacteria. Apply warm and cold compresses for the relief of gum pains. Apply cold compress to relieve gum pain and swelling. Getting enough water for saliva.
What causes inflammation of the gums?
It can often be caused by gingivitis as well as other conditions — nutritional deficits, hormone changes and infections. Swollen gingivitis can sometimes be painful or painful.
Yes, if you treat it properly the swelling of the gums play the gums sore the mouth should fade. Sometimes swelling is able to improve itself. Generally the swelling of the gums should subside when removing crumbs and food particles first. However, the swollen gums can cause a painful headache.
Which medicine is best for gum swelling?
In some patients, the medication is used to relieve the pain caused by tooth decay and gum disease. The best outcomes can be seen when using prescription pain relievers in addition to home remedies.
How can I get rid of swollen gums?
Treatment of a sore or swollen gum. Use salt water to rinse out bacteria and toxins. Apply hot compress for gum inflammation. Cold compression helps prevent gum ache. Drinking enough water stimulates blood sugar production.
